7 Ways To Use Semantic SEO For Higher Rankings

Over the years, search engines like Google have used semantic analysis to understand human language more deeply and provide users with more relevant search results.
For this reason, a single keyword approach to SEO is no longer sufficient.
Instead, semantic SEO takes into account the deep learning and natural language processing algorithms that Google relies on.
Site owners who use semantic SEO strategies are more likely to build positional authority in their industry.
They can also outpace competitors more easily for important keywords in their niche.
What is semantic seo?
Semantic SEO is the process of building more meaning and objective depth into web content.
By doing this, you help Google’s crawlers better understand your content.
You also help them see it as high quality and thus promote it more often in SERPs.
Semantic SEO and Google
In the early days of SEO, Google’s ranking algorithm was less advanced.
Crawlers simply looked for specific keywords on the page to understand meaning and relevance.
But we all know that there is a lot more that goes into understanding human language than just the words we use.
Context, facial expression, tone, and the paragraphs before and after our words all influence their meaning.
This is why Google has striven to take a more human-like and semantic approach to understanding and ranking web content.
Some of the biggest turning points in this effort include:
- Knowledge Graph: large and sophisticated The knowledge base used by Google Crawlers help understand relationships between specific entities and concepts.
- Hummingbird: A 2013 algorithm update helps Google better understand meaning and the context behind the queries, which reduces focus on single keywords.
- brain rank: a 2015 A machine learning algorithm that helps Google better interpret your search intent Thus providing users with more relevant search results.
With these developments, Google can look at a piece of content and understand not just what topic it’s about, but related subtopics, terms, entities, and how all these different concepts interrelate.
How semantic SEO improves the search experience
Why so much focus on semantic SEO?
Well, Google always tries to make search better for users.
In fact, researchers aren’t necessarily looking for one definitive answer when they use Google; They often try to understand a particular topic in more depth.
For example, suppose a user types the phrase “What are the inbound links”?
Most likely, they will have additional questions that pop up after they find their answer, such as:
- How do I get backlinks?
- Where can I get backlinks?
- How many backlinks do I need?
- Can I buy backlinks?
- What is the difference between white hat and black hat associations?
- And others!
In terms of the search experience, it is much better for the user to find a single piece of content that answers all those related questions rather than separate pieces of content for each individual question.
In general, Semantic SEO improves the search experience for users.
It allows them to get more in-depth information without having to repeatedly return to the search bar.
The benefits of semantic SEO
Although semantic SEO strategies require more time and effort on the part of the content teams, the benefits are significant.
- More keyword rankings in organic search.
- Improve content quality signals in the eyes of Google’s crawlers.
- Brand strength and expertise in the eyes of researchers.
- Helping Google see your brand as its own with expertise on core topics.
- Traffic ranking or people also ask features.
- More opportunities for internal linking.
- Keeping users on your website longer rather than coming back to search.
By creating linguistically and thematically rich content, site owners can see significant improvements in overall SEO performance.
7 Semantic SEO Strategies for Getting Higher Rankings
Semantic SEO encompasses many strategies that you may have already heard of or incorporated into your SEO campaigns.
Combined together, they all focus on improving topical depth and better conveying the meaning of web content.
1. Optimize keyword combinations
Since Google does not rely on just one keyword per page, your content team must optimize your web pages for multiple keywords in the same semantic group.
Keyword clusters are groups of similar keywords that share a semantic relevance.
By optimizing these keyword combinations, you can improve the total number of keywords your content ranks for and build more meaning into your content.
Here is an example of what keyword groups in a content strategy might look like:
-
Screenshot from Google Sheets, February 2022
In fact, Google already ranks our landing pages for multiple keywords anyway.
Keyword clustering relies on leveraging the powerful semantic capabilities of Google to improve the total number of keywords that our content ranks for.
This means more opportunities for organic clicks.
2. Optimize topical depth and content length
The simplest semantic SEO strategy is to increase the length of your web content by offering a more comprehensive exploration of your topic.
Although content length is not formally a ranking factor, longer content is likely to display stronger semantic cues.
Also, several studies have shown the strong association between longer content and higher ranking sites.
-
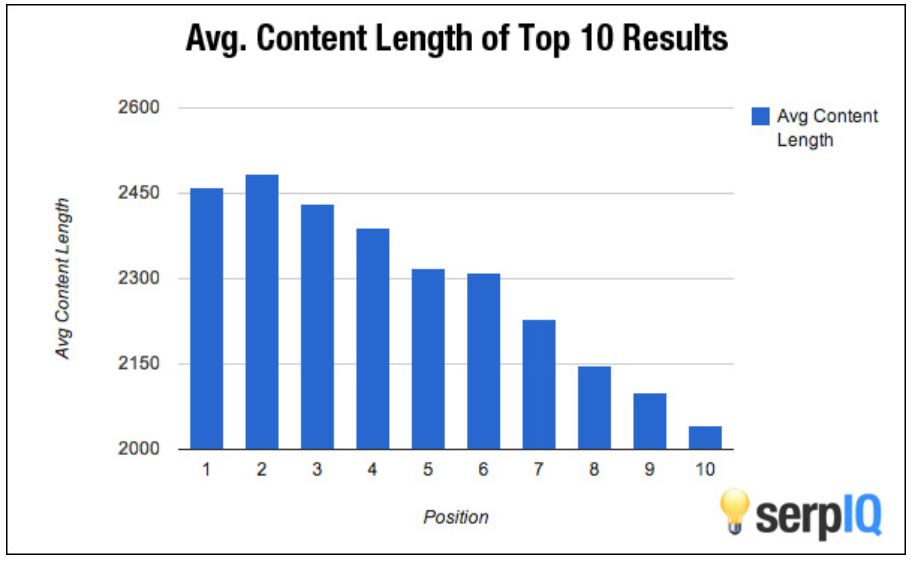 Image courtesy of sweor.com, February 2022
Image courtesy of sweor.com, February 2022 - But simply relying on keyword stuffing or repetition to improve content length will not be effective.
Instead, the best way to increase the length of your web content is to be more specific, accurate, and in-depth with the information you give users about the underlying topic.
3. Include synonyms and related terms
With Google’s optimized algorithms and NLP models, there is no need for users to fill in their entire content with their keyword target in order to rank.
Thanks to semantic analysis, Google is smart enough to understand synonyms and related terms.
It’s not a ranking factor, however adding these terms to content via page titles, meta descriptions, h1-h6s, and image alt text can improve topical depth and semantic cues, while making content more readable and accurate for searchers.
4. Answer people and also ask questions
Another way to improve the semantic depth of your content is to answer common questions users have regarding your primary keyword.
-
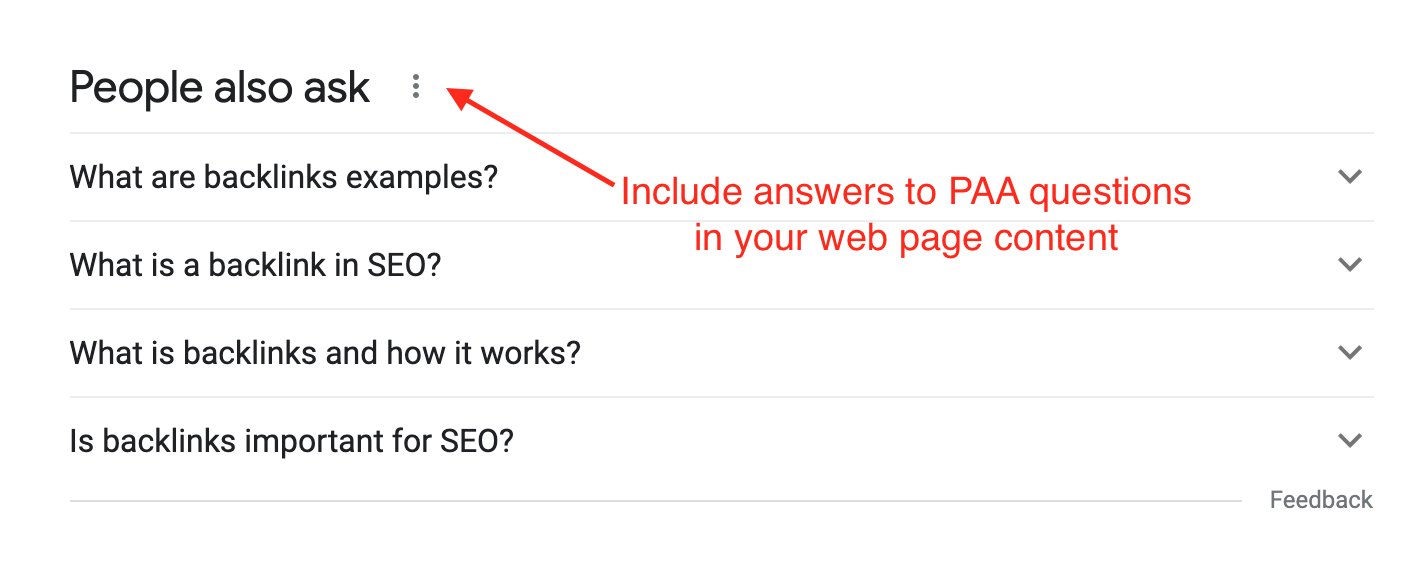 Screenshot from Google, February 2022
Screenshot from Google, February 2022
According to a recent study of 2.5 million search queries, Google’s “People Ask” feature now appears 48.4% For all search queries, most often above position 1.
By answering these questions in your web page content, you not only improve your semantic signals, but also give your page the opportunity to rank at the top of the SERPs.
Web pages for PAA questions can appear even if the blue link result appears on page 2!
5. Add structured data
Although not often considered a semantic SEO strategy, structured data is about conveying the meaning of content directly to Google’s crawlers.
Structured data describes the function, object, or content description.
For example, when you use the Products schema on a product page, you instantly pass on to Google a variety of important details.
It includes information such as type, dimensions, color, size, etc.
When paired with other semantically relevant or topic-rich content on your web page, the purpose and meaning of your web content is unmistakably clear to search engines.
6. Use content optimizer tools
Content Optimizer tools do the hard work of identifying all the linguistically related terms for you.
They basically provide “cheat codes” to improve topical depth.
-
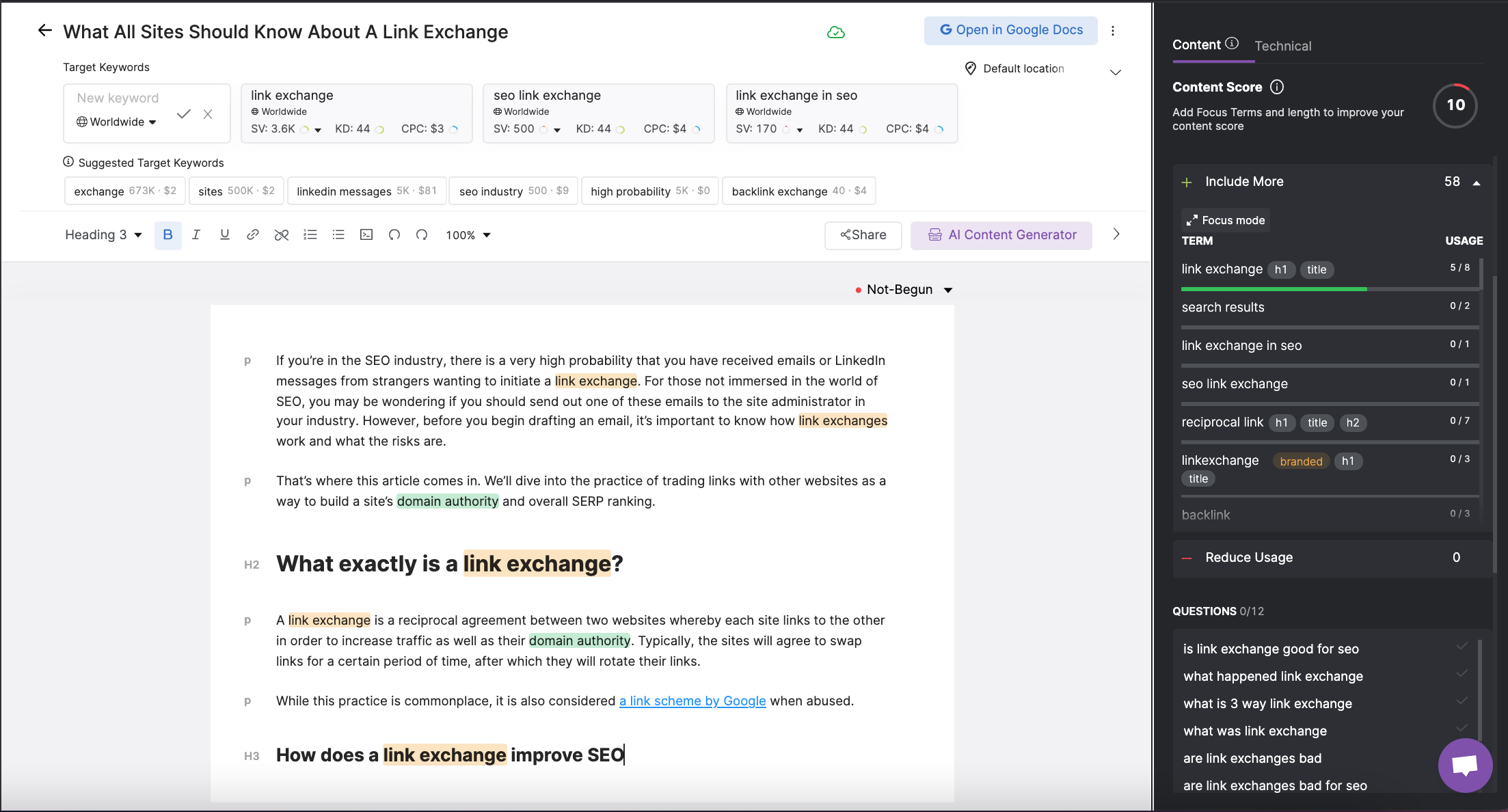 Screenshot from SearchAtlas, February 2022
Screenshot from SearchAtlas, February 2022
An SEO content writer can certainly investigate the first page ranking of content to identify important terms.
But content optimization software does the same job in a matter of seconds.
By adding these terms, topics or questions to the page, you can improve the depth of the topic and thus the practice of semantic SEO.
7. Build theme groups on your website
Unlike keyword groups, topic groups focus on more than just one piece of content.
Topic groups are collections of content pieces around a central topic.
For example, the group of keywords pictured in Strategy #1 is part of a larger topic group focused on link building.
The different articles (each targeting their own set of keywords) all link to the basic “canonical page,” which focuses on the larger topic of link building.
-
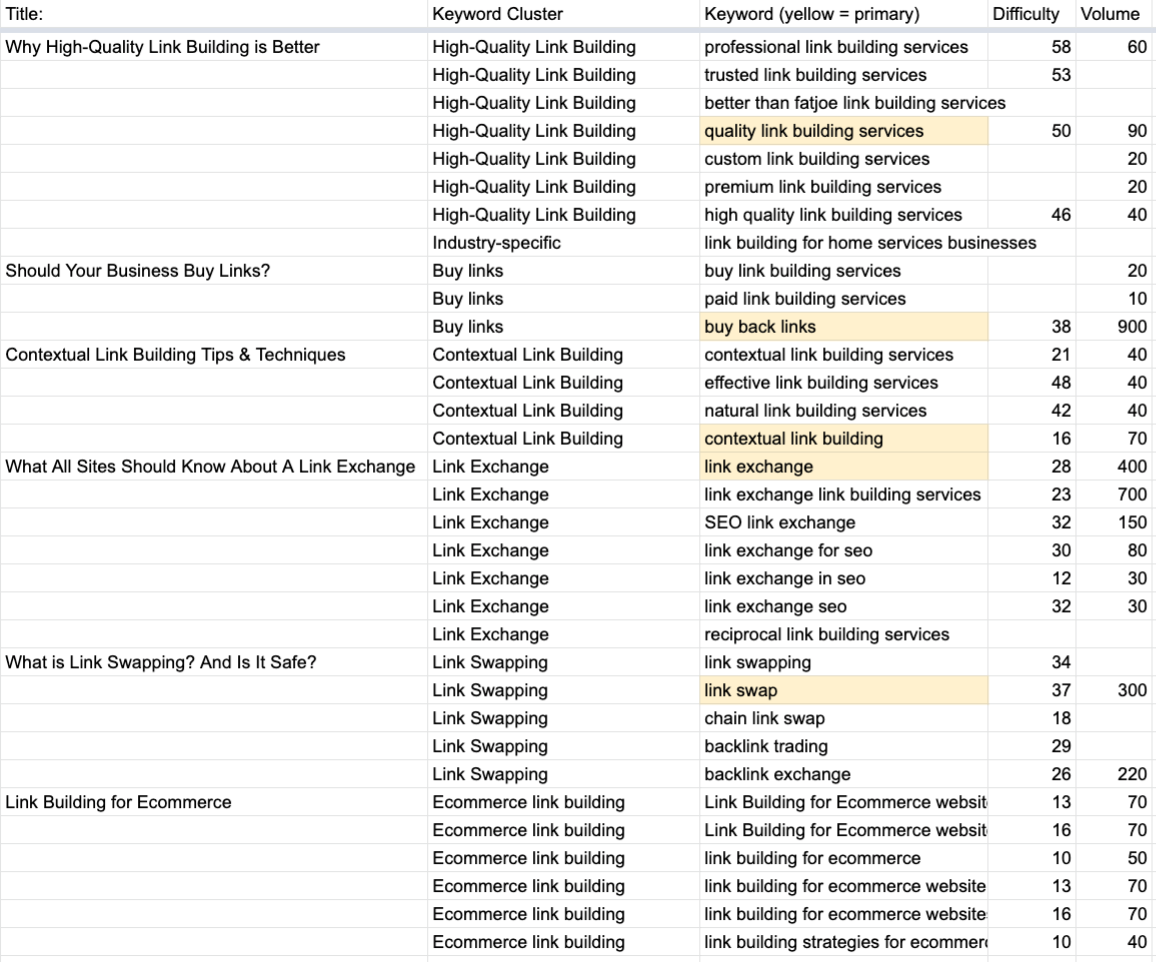 Screenshot from Google Sheets, February 2022
Screenshot from Google Sheets, February 2022
The purpose of these three-dimensional subject groups:
- First, improve your semantic SEO signals and meaning.
- Second, improve the total number of keyword rankings.
- And third, establish this site as an authority on “link building.”
The number of theme groups on your website depends on the products or services your brand offers.
Final thoughts on semantic SEO
Again, semantic SEO involves a variety of strategies and concepts, but they all focus on meaning, language, and search intent.
SEO experts can leverage semantic SEO strategies to highlight semantic signals that Google’s algorithms are trained to identify.
By doing this, Google will associate your website with not just a few keywords, but several larger topics – and thousands of keywords and search queries related to them.
More photos:
- Semantic Search: What It Is and Why It Matters for SEO Today
- What is latent semantic indexing and why does it matter to SEO?
- The Complete Guide to On Page SEO
Featured image: pogonici/Shutterstock




