Google Autocomplete: A Complete SEO Guide

Google Autocomplete is a controversial but powerful search feature.
When you type a word, or even a letter, into Google, it populates a list of search suggestions. That’s what autocomplete is.
SEO professionals, paid search marketers, content marketers, and social media managers can all benefit from using Google Autocomplete to assist with various keyword-focused and intent-searching projects.
On the other hand, Google autocomplete often makes the news for funny, strange, or even offensive habits (Mostly in a negative way).
People use autocomplete constantly, saving thousands of seconds every day, but it’s also been blamed for political cover-ups and spoiling movies, TV shows, and video games.
Google Autocomplete can also be a powerful marketing tool. SEO professionals and other digital marketers have used them for years to inform strategy, get keywords and find the important questions customers are asking.
They can use autocomplete to better optimize the numerical characteristics of customers, the content, and the messages that compose them.
This guide will help you understand the true power that this simple but very useful feature can offer to help with your daily tasks.
What is google autocomplete?
Google’s Own Words Google’s autocomplete feature is designed “to make it faster to complete searches that you start typing.”
It’s integrated across Google Search and other Alphabet properties that use Google, including the Omnibox on Chrome.
Google estimates, cumulatively, Provides more than 200 years from writing every dayand on average reduces overall typing by about 25 percent.
The primary purpose of the autocomplete dropdown is to reduce the time a user spends typing by providing predictions of what the user might be typing – including for websites that use the built-in Google tool Custom Search Engine Feature.
Although autocomplete has been a desktop search feature since late 2004, it’s becoming more useful as a time-saving feature on mobile devices.
Typing on a mobile device is a bit more difficult than doing it on the larger keyboards we’ve grown used to, so it’s a welcome tool of help and time-saver for many.
There are many other useful ways the feature can be used to leverage content ideas, keyword suggestions, intent exploration, online reputation management, and other data-driven tasks.
How does autocomplete work?
Former Google employee Kevin Gibbs devised the project, which was originally called “suggest googleBy another former Googler, Marissa Mayer.
Since then, Google has moved away from the “Suggest” name because it doesn’t always make the most thoughtful, interesting, or relevant predictions.
Google calls completions that make “predictions,” not “suggestions.” This is because of how autocomplete works.
The autocomplete feature is supposed to help people complete the sentence they meant — not indicate search intent, as with “I feel lucky.” They set predictions by looking at popular searches on Google, including looking at popular searches that might be relevant.
This allows autocomplete to quickly update and adapt to new search trends and news stories.
Much of the autocomplete behavior is computer generated, collecting data from millions of other Google searches and their results, including the content on those pages. It also takes information from your search history, location, and other data points.
Google has also put a lot of work into avoiding inappropriate or offensive autocomplete suggestions. This means that there are automatic and manual removal actions that can affect remaining autocomplete suggestions.
Autocomplete is also relevant to the knowledge graph, especially on mobile, and can make knowledge graph suggestions in prediction.
Google didn’t build AutoComplete into its default search engine until 2008 (previously it was a subscription feature).
The best ways to use Google Autocomplete
1. Keyword research
It’s a long, tedious, and arduous task, but it’s also the foundation of all SEO strategies—and it has been for a long time.
While we may not explicitly target keywords, keywords and the ideas associated with them will always be an important part of search marketing.
Keyword research is one of the first tasks addressed at the beginning of the engagement—and carried out throughout the engagement—to understand not only the brand and the content you’re creating, but also potential shortcomings, website strengths and weaknesses, and content gaps.
Autocomplete doesn’t do all the work for you in terms of keyword research, but it’s a great place to start or use it early and often when developing content calendars and general organic search strategies.
Using it (along with other keyword resource tools like Google Keyword Planner and other third-party keyword databases) to get an idea of the right keywords you want to target by considering monthly search frequency, competition, and even cost-per-click (CPC) Pricing will do justice to your search strategy.
One of the great benefits of Google Autocomplete is its ability to detect long, high quality phrases that are commonly searched across the web.
Because the primary measure of autocomplete is popularity—based on real searches that users perform in real time—the value of autocomplete lies in the sheer amount of keyword-level data you can search for if you work hard and long enough.
As always, be sure to sign out of Google to ensure that personalization is restricted for an unbiased look at predictions.
Long-tail keywords are incredibly useful when filling content gaps but also offer endless possibilities in terms of high-value blog posts and educational content in a brand niche.
2. Exploring intention
Understanding user intent is important as it guides the page’s purpose, message, layout, and even images. We know that pages perform best when they exactly meet the user’s intent for a search query.
You can use autocomplete to better understand user intent, but doing so can be tedious and tedious. Taking the time to visit many different web pages in search results associated with specific predictions will take some time, focus, and content consumption. But the information you can extract from this method is invaluable.
Keywords overlap different stages of user intent, and without more keyword context it can be difficult to understand the intent.
Autocomplete will help you not only understand long-form high-value keywords and the intent around them, but it will also help marketers learn about the volume of content around certain intent stages, as well as which long-term phrases and intent stages can be optimized as a higher priority.
Of course, for high-value keywords — long or traditional one-, two-, or three-word phrases — it’s important to meet all stages of intent as they relate to high-value keywords.
This is the idea behind a high-quality, comprehensive search strategy. And autocomplete can help you get there.
3. Online Reputation Management
Autocomplete has been important in the field of online reputation management as well.
Remember, when a user searches for your name or brand name, the first thing they see, even before your site on the SERP (search engine results page), are the autocomplete predictions associated with that name.
If these expectations are negative, or even if one of them is negative, it can have a real impact on your business performance.
think about it. you are looking [Dog Washers Inc] And the first prediction ends with “losing the dog.” You probably won’t feel too keen on bringing your dog there for his next bath.
Same for a restaurant; If you search [Ted’s Seaford Spot] And the prediction ends with, “e. Coli,” I have a pretty good idea what you’re not eating tonight.
Autocomplete is an important part of Online Reputation Management (ORM) and cannot be overlooked when working to balance all the negative communications being made with brands.
One has to be vigilant, just like most HRM strategies. Several ways brands can work to offset negative autocomplete expectations are:
- Control your brand conversations to ensure the right connections are made in Google Autocomplete.
- Social media account optimization promotes positive links that may be overshadowed by negative links.
- Social media content, messaging, and engagement are in line with the above improvements and brand voice and tone.
- Branding and consistent messaging for profile sites with positive keyword association used elsewhere
- Start small and make an impact by finding positive brand links from different sites. Obviously, the more people, the better. But you’d be amazed at the impact it can have.
- Build backlinks to Google SERPs to get positive associations for keywords in your name; things like [sam hollingsworth seo writer] And the [sam hollingsworth handicapper] It would be a great start for someone like me. 😊
- If there are negative autocomplete suggestions, make sure you have a strategy for how to address them.
4. Content Creation and Exploration
You can now also use autocomplete to generate content and scout competitor content for your own content ideas. It’s easy and fun to use the autocomplete feature in conjunction with other online writing tools, to see what web users are searching for.
questions and answers
Just looking at the who, what, where, when, and why with a few branding questions can get you to a lot of FAQs—questions that people might actually be looking for.
related words
You can do this in many ways and for many reasons. The easy way is to “compare brand name” – Google will auto-fill with competitors. You can also look at Brand Name and see what autocomplete finds there – finding ways to expand your brand.
Related topics
If you can find autocomplete suggestions for related topics, which are not covered by your main topic, you may have an advantage to develop some content in that niche.
Queries like “how* does it work” can be invaluable, and autocomplete fills the wildcard space with suggestions. You can also do this to find questions about your brand, questions for content marketing, find issues potential customers are searching for, and even see if users are searching for certain social media accounts.
Autocomplete policies
With a history of backlash over some of its search predictions, Google is working hand in hand to prevent inappropriate autocomplete predictions when it comes to:
- Explicit sexual predictions.
- Predictions of hate against groups and individuals.
- violent predictions.
- Dangerous and harmful activities in the forecasts.
It may also remove predictions that could be considered spam or facilitate or advocate hacking, or if a legal requirement to do so is made.
Google states that it removes predictions that relate to any of the above situations unless they contain non-harmful medical or scientific terms.
Looking for feedback
To better control inappropriate autocomplete predictions, Google has launched its own feedback tool and uses the data to continually make improvements.
For example, it is not necessary that a particular demographic be targeted for something inherently repugnant; And the comments help to find out faster and easier.
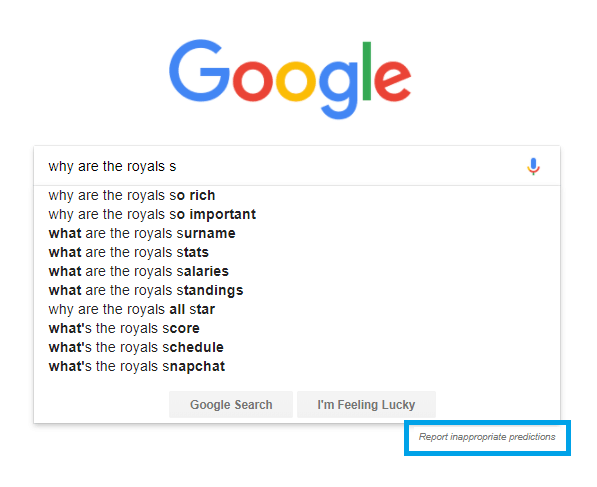 Google search screenshot, November 2021
Google search screenshot, November 2021Understanding what people are actually searching for is an essential part of your SEO strategy.
Learn how to integrate Google Autocomplete into your search. You might be surprised at the specific keywords and search intent they reveal!
More SEO resources:
- 28 free tools to help you find what people are looking for
- Google will remove more types of autocomplete predictions
- Google is looking for feedback on autocomplete suggestions
Featured image: Shutterstock / Fonstra


![Optimize Your SEO Strategy For Maximum ROI With These 5 Tips [Webinar]](https://altwhed.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Optimize-Your-SEO-Strategy-For-Maximum-ROI-With-These-5-390x220.jpg)

