A Comprehensive Guide To Marketing Attribution Models

We all know that customers interact with a brand through multiple channels and campaigns (online and offline) along the conversion path.
Surprisingly, in the B2B sector, the average customer is exposed to a brand 36 times before becoming a client.
With so many touch points, it is difficult to say how much influence a marketing channel or campaign has on a purchasing decision.
This is where marketing attribution comes in.
Referral marketing provides insight into the most effective touch points along the buyer’s journey.
In this comprehensive guide, we simplify everything you need to know to get started with marketing referral forms, including an overview of your options and how to use them.
What is marketing attribution?
Marketing attribution is the rule (or set of rules) that describes how conversion credit is distributed throughout the buyer’s journey.
How much contribution each touchpoint should receive is one of the more complex marketing topics, which is why so many different types of referral models are used today.
6 common attribution models
There are six common referral models, and each distributes conversion value across the buyer’s journey differently.
Don’t worry. We’ll help you understand all of the models below so you can decide which one is best for your needs.
Note: The examples in this guide use cross-rule-based Google Analytics 4 models.
Rules-based cross-channel means that it ignores direct traffic. This may not be the case if you are using alternative analytics software.
1. Last click
The last click referral model gives all the credit for the marketing touch point that happens right before conversion.
Last Click helps you understand which marketing efforts lead to closing sales.
For example, a user initially discovers your brand by watching a YouTube ad for 30 seconds (interactive view).
Later that day, the same user Googled your brand and clicked on an organic search result.
The following week, that user views a retargeting ad on Facebook, clicks on, and signs up for our email newsletter.
The next day, they click through the email and convert into a customer.
Under the last click referral model, 100% of the credit for that conversion is given to the email, the point of contact that closed the sale.
2. First click
First click is the opposite of the last click attribution form.
All credit is given for any conversion that may occur for the first interaction.
First Click helps you understand the channels that create brand awareness.
It doesn’t matter if a customer clicked on your retargeting ad and later converted through an email visit.
If the customer initially engages with your brand through an interactive YouTube view, the paid video will get the full credit for that conversion because it started the journey.
3. Linear
Linear attribution provides insight into your marketing strategy as a whole.
This form is especially useful if you need to maintain awareness throughout the entire buyer journey.
The transfer balance is divided equally among all channels with which the customer interacts.
Let’s look at our example: each of the four touchpoints (paid video, membership, paid social, and email) all get 25% of the conversion value because they’re given equal credit.
4. Time decay
Time decay is useful for short sales cycles such as merchandising because it takes into account when each touch point occurs.
The first touch gets the least amount of credit, and the last tap gets the maximum.
Using our example:
- Paid video (engaged view on YouTube) will get 10% credit.
- Organic searches will get you 20% off.
- Paid Social (Facebook Ad) You get 30%.
- Email, which occurred on the day of conversion, gets 40%.
Note: Google Analytics 4 distributes this credit using a seven-day half-life.
5. The standing position
The position-based (U-shaped) approach divides the credit for the sale between the two most important interactions: how the customer discovered your brand and the interaction that led to a conversion.
Using position-based referral models, both paid video (interactive viewing on YouTube) and email would get 40% of the credit because they were the first and last interaction in our example.
Organic search and Facebook ad will each get 10%.
6. Data Driven (via Linear Channels)
Google Analytics 4 has a unique data-driven attribution model that uses machine learning algorithms.
The contribution is set based on how each touchpoint changes the estimated conversion probability.
Uses each advertiser’s data to calculate the actual engagement contribution for each conversion event.
The best marketing attribution model
There isn’t necessarily a “best” marketing referral model, and there’s no reason to limit yourself to just one.
Comparing performance under different referral models will help you understand the importance of multiple touch points along the buyer’s journey.
Compare Models in Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
If you want to see how performance changes by attribution model, you can easily do that with GA4.
To access Model Comparison in Google Analytics 4, click on “Advertising” in the left menu and then click on “Model Comparison” under “Attribution”.
By default, the conversion events will be all, the date range will be the last 28 days, and the dimension will be the default grouping of channels into groups.
Start by selecting the date range and conversion event you want to analyze.
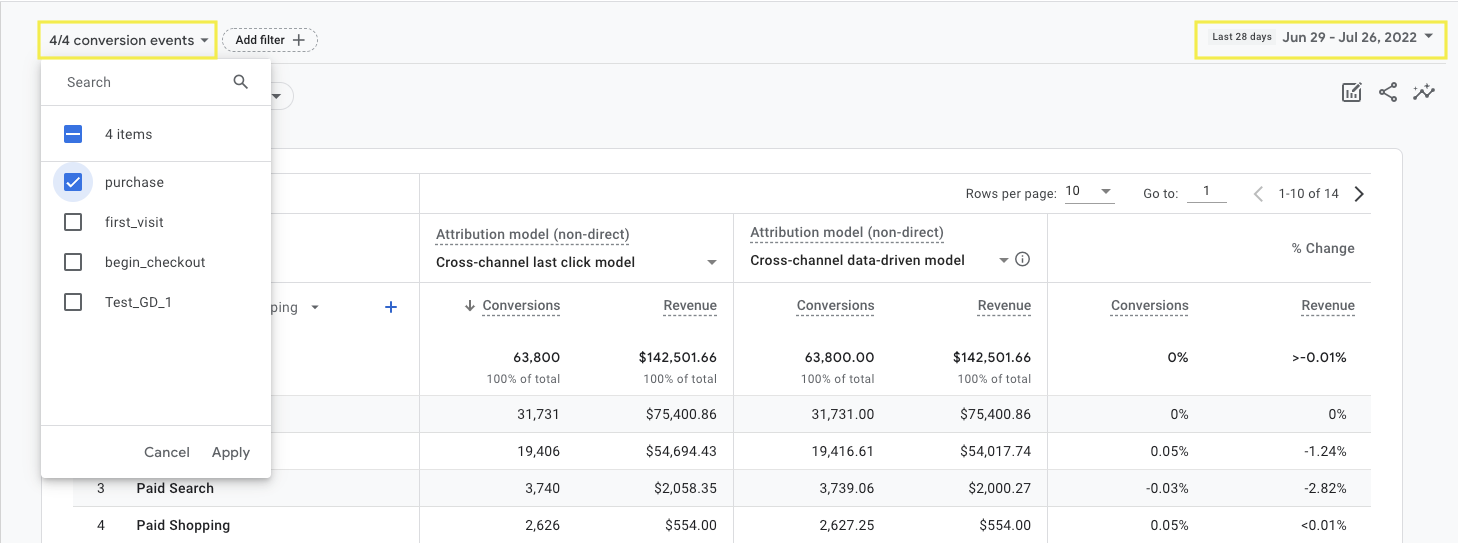 Screenshot from GA4, July 2022
Screenshot from GA4, July 2022You can add a filter to show a specific campaign, location or device using the Edit comparison option at the top right of the report.
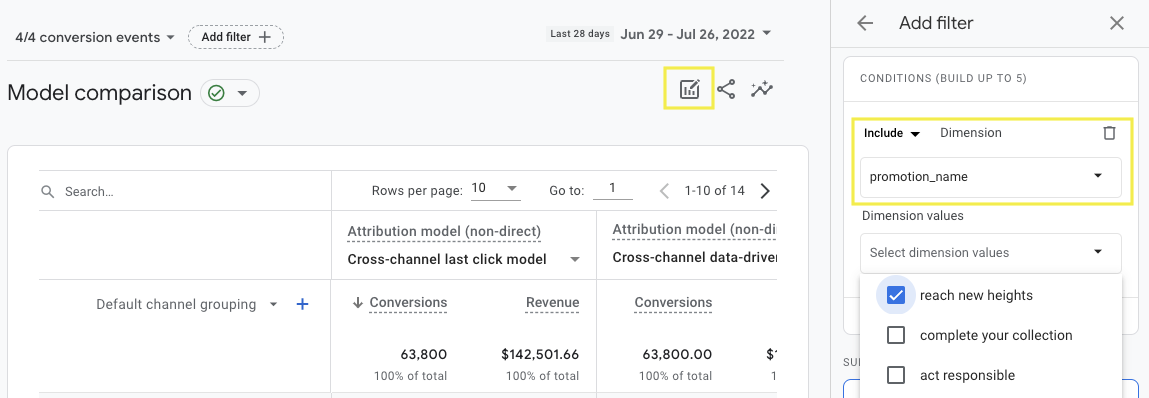 Screenshot from GA4, July 2022
Screenshot from GA4, July 2022Select the component to report on and then use the dropdown menus to select referral models for comparison.
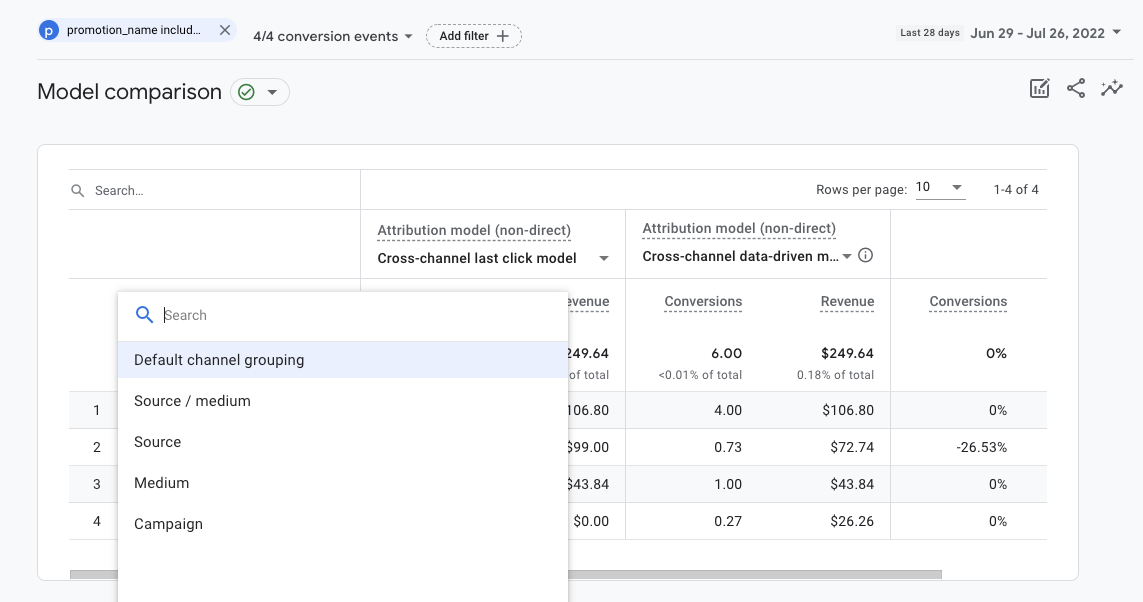 Screenshot from GA4, July 2022
Screenshot from GA4, July 2022GA4 model comparison example
Let’s say you are asked to drive new customers to your website.
You can open Google Analytics 4 and compare the “last click” model with the “first click” model to discover which marketing efforts start customers down the conversion path.
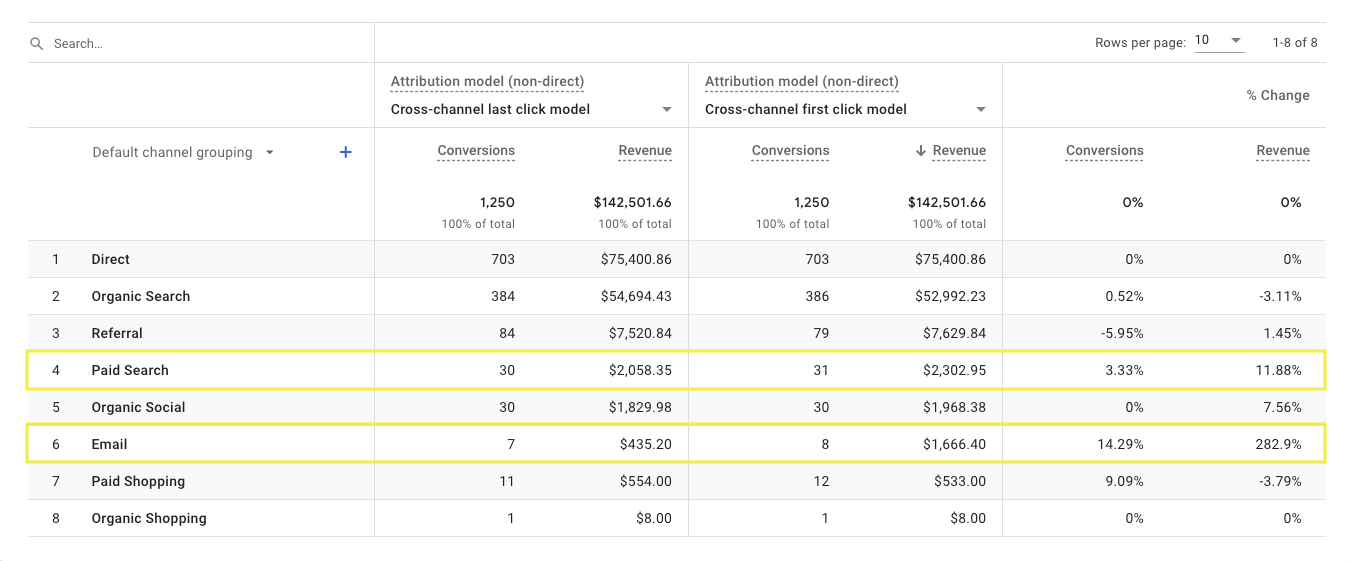 Screenshot from GA4, July 2022
Screenshot from GA4, July 2022In the example above, we might opt for more email and paid search because they seem to be more effective at getting customers started down the funnel than closing a sale.
How to change the Google Analytics referral form 4
If you choose a different referral model for your company, you can edit your referral settings by clicking the gear icon in the bottom right corner.
Opens Referral settings under the property column and click Report referral form Drop-down menu.
Here you can choose from the 6 channel referral models discussed above or the ‘preferred last click ads model’.
Ad preference gives full credit to the last Google Ads click along the conversion path.
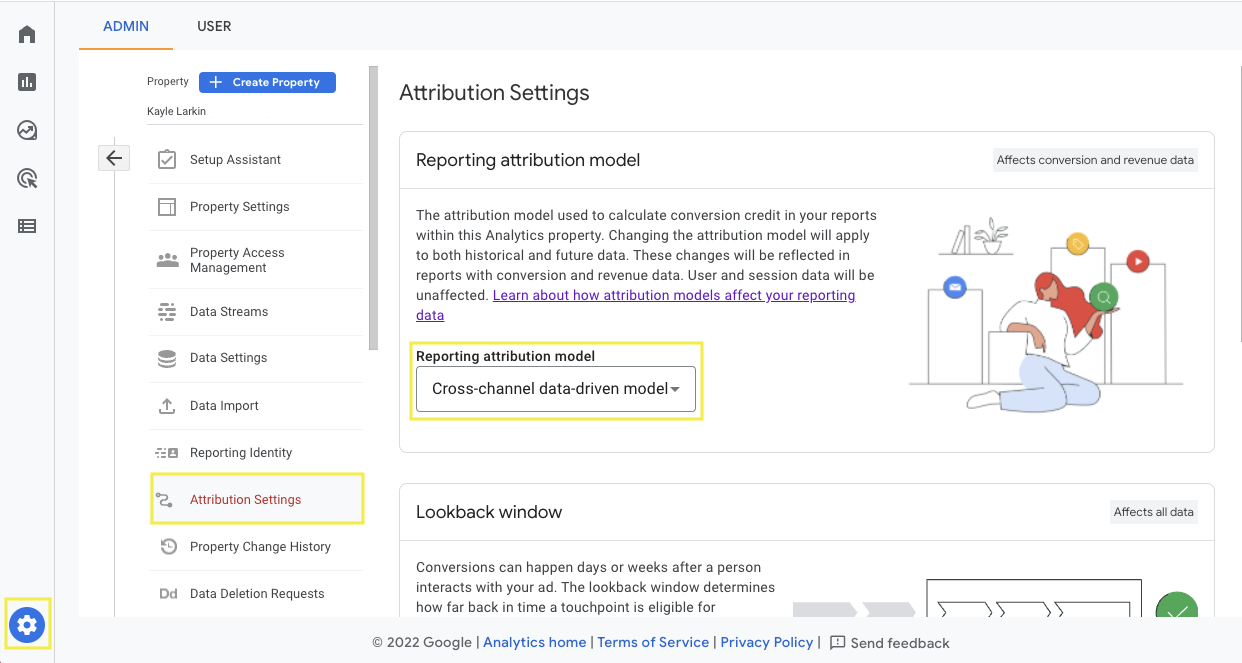 Screenshot from GA4, July 2022
Screenshot from GA4, July 2022Please note that changes to the attribution model will apply to past and future data.
Final thoughts
It’s easy to determine where and when a transaction or purchase occurred. The hard part is determining the reason behind the purchase or purchase.
Comparing attribution model reports helps us understand how the entire buyer journey supports conversion.
Looking at this information in greater depth enables marketers to increase their return on investment.
Got questions? Let us know Twitter or linkedin.
More resources:
- Complete Guide to Multi-Touch B2B Referral Forms
- Here’s what happens when you change attribution models in Google Ads
- A Complete PPC Marketing Guide for Beginners
Featured image: Andrii Yalanskyi/Shutterstock




